Data analysis
Certainly! Data analysis involves the process
of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and
modeling data to uncover useful
information, draw conclusions,
and support decision-making.
Here's an overview of key steps
and concepts involved in data analysis:
Data analysis
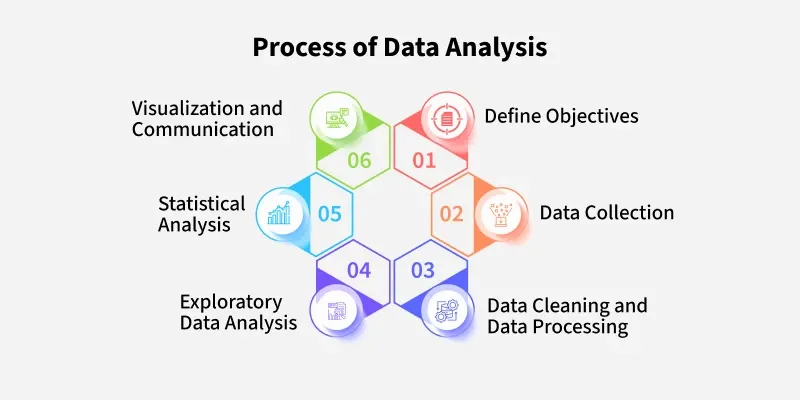
1. **Define Objectives**
Understand the purpose of the analysis.
Identify questions you want to answer
or problems to solve.
2. **Data Collection**
Gather relevant data from various sources
such as databases, spreadsheets, surveys, or APIs.
3. **Data Cleaning**
- Handle missing values.
- Remove duplicates.
- Correct errors and inconsistencies.
- Normalize or standardize data if necessary.
4. **Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)**
Summarize data using descriptive statistics (mean,
median, mode, standard deviation).
Visualize data through charts like
histograms, scatter plots, box plots.
Detect patterns, trends, or anomalies.
5. **Data Transformation**
- Create new variables or features.
- Encode categorical variables.
- Scale or normalize data to prepare for modeling.
6. **Modeling and Analysis**
Choose appropriate statistical or machine
learning models.
Train models on the data.
Validate models using techniques like cross-validation.
7. **Interpretation**
- Analyze model outputs.
- Draw meaningful conclusions.
- Understand the implications of findings.
8. **Reporting**
Present insights through reports, dashboards,
or visualizations.
- Communicate findings to stakeholders effectively.
**Tools and Languages Commonly Used:**
- Programming Languages: Python (pandas,
NumPy, scikit-learn, matplotlib, seaborn),
- Software: Excel, Tableau, Power BI, SAS
- Databases: SQL
**Best Practices:**
- Ensure data privacy and security.
- Maintain reproducibility of analysis.
- Document your methodology.

Advanced data analysis:
Advanced data analysis in education involves leveraging
sophisticated statistical, computational, and machine
learning techniques to extract meaningful insights from
complex educational data. This approach enhances
decision-making, personalized learning, policy formulation,
and overall educational effectiveness. Key aspects include:
Learning Analytics and Educational Data Mining :
Analyzing student interaction data from Learning
Management Systems (LMS) to identify patterns
inengagement and performance.
Predicting student success, dropout risks, and
identifying at-risk populations through predictive modeling.
Psychometric and Assessment Data Analysis:
Applying Item Response Theory (IRT) and Rasch models
for precise measurement of student abilities and test
item functioning.
Conducting fairness and bias analysis in assessments.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Analyzing open-ended responses, discussion forums,
and essays for sentiment, topic modeling, and comprehension levels.
Automated feedback generation and automated essay scoring.
Machine Learning and AI:
Personalizing learning paths based on individual learner
profiles using clustering, classification, and reinforcement learning.
Adaptive testing systems that dynamically adjust difficulty levels.
Data Visualization and Dashboarding:
Creating interactive dashboards for educators and
administrators to monitor performance metrics, attendance,
engagement, and other key indicators in real-time.
Big Data Integration:
Combining data from various sources such as
demographic data, socio-economic indicators,
and institutional records for comprehensive analysis.
Ethical Considerations and Data Privacy:
Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations
(like FERPA, GDPR).
Addressing biases in data and ensuring equitable analysis.
Applications of Advanced Data Analysis in Education:
Designing targeted interventions for students who need
additional support.
Improving curriculum design based on learning outcome
data.Informing policy decisions with evidence-driven
insights.
Enhancing teacher training through feedback
analytics.
Emerging Trends:
Use of AI-powered virtual tutors and chatbots.
Real-time analytics for immediate instructional adjustments.
Incorporation of adaptive learning technologies driven by data insights.
Summary
In summary, advanced data analysis in education
empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions,
foster personalized learning environments, and ultimately
improve educational outcomes through data-driven
strategies.






.png)

